Contents
- Introduction
- General Information
- Contact Center Configuration Process
- Initial General Configuration
- Inbound Voice and Chat Service Configuration
- Outbound Campaign Configuration
- Email Service Configuration
- Users and Teams
- Overview
- Users
- Forwarding and Voicemail Operation
- Teams
- Agent Dashboard Metrics
- Roles
- Privileges
- Skill Levels
- Help Screens
- Directory
- Scenario Entries
- Scenarios
- Services and Campaigns
- Services and Campaigns Overview
- Properties Tab
- Assignments Tab
- Lists Tab
- Dispositions Tab
- Activity Tab
- Numbers Tab
- Service Level Tab
- Outbound Tab
- Results Tab
- Archive Tab
- Canned Tab
- Email Tab
- Pre-defined Dispositions
- Outbound - General
- Outbound - Calling Hours
- Outbound - Dial Rules
- Outbound - DNC
- Outbound - Diagnostics
- Activity Forms
- Lists
- Tasks
- Call Center Configuration
- General Settings
- Integration Accounts
- Knowledge Base
- Calendars
- Hours of Operation
- State Calling Hours
- Auxiliary Skills
- Audio Treatments
- Shared Voice Segments
- Voicemail
- Omni-Channel Routing
- Chat Settings
- Email Settings
- Quality Management
- Reporting
- Security
- Appendices
The logic of processing of an inbound email interaction is initially determined by the email address that was used by the email sender. In the simplest case, such email addresses can correspond to your email services (e.g., your sales@company-name.com and support@company-name.com may be associated with your Sales and Support services respectively). In a more complex configuration, you may want to apply some keyword-based analysis of email texts to associated emails with appropriate services (e.g., an email coming to support@company-name.com can be further categorized into Smartphone Support and Tablet Support services based on the presence of the words phone and tablet in the text of email messages).
The logical entity that describes association between email addresses and keywords on the one hand and email services on the other hand is called email scenario entry. Unlike the other types of scenario entries, the email entries do not currently refer to any actual scenarios. All information required for association of incoming emails with services in the current release is contained in the configuration settings of the email entries themselves.
Note that before you configure an email scenario entry, you should set up a corresponding email service. If you plan any keyword-based categorization, it may also be easier to define upfront all of the known services that the emails arriving via this entry may be attributed to. Once the email entry is set up according to your initial needs, you can add more services and update the categorization rules at any time.
- Note: ServicePattern stores all processed emails for activity history, reporting, and quality management purposes. These storage practices may not coincide with the general email retention policies of your organization. For compliance with such general retention policies, we recommend that you always store copies of all emails received to and sent from the email addresses used for email scenario entries.
To set up and manage email scenario entries, select the Email option from the Scenario Entries menu.
- Note: This option is visible and available to you only if the email management capability is enabled for your contact center at the service provider level.
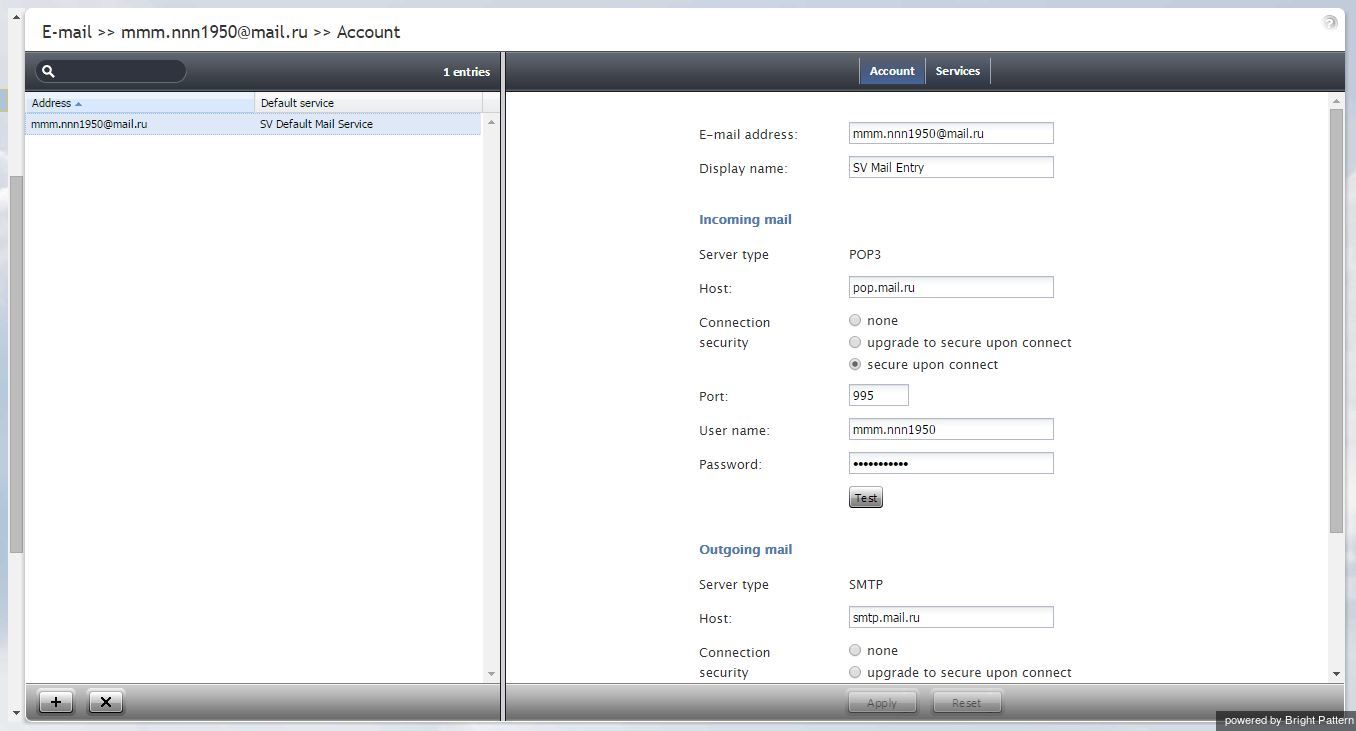
The Email Scenario Entries screen properties are described in the following table:
| Account tab | |
|---|---|
| Email address | Email address that the customers will use to send emails to a specific service or a range of services. This address will also appear in the From: field of corresponding email replies as well as any outbound emails related to services associated with this scenario entry. This parameter is mandatory |
| Display name | Display name for the above email address. This parameter is mandatory |
| Incoming Mail, Server type | Type of the server used for retrieval of incoming mail arriving to the mail box associated with the above address. Read-only. Currently the POP3 protocol is supported. |
| Outgoing Mail, Server type | Type of the server used for transmission of email messages from the above address. Read-only. Currently the SMTP protocol is supported. |
| Host | Name of the host where the above server is run. This parameter is mandatory |
| Connection security | Indication whether a cryptographic protocol (TLS or SSL) will be used to secure this connection. For a non-secure connection, select none. To negotiate encryption in a plain connection, select negotiate encryption in a plain connection (STARTTLS). For an immediate secure connection, select use an encrypted connection (TLS/SSL v3). |
| Port | Port assigned to the above server on the above host. This parameter is mandatory. |
| Username | User name for email client authentication. This parameter is mandatory. |
| Password | Password for email client authentication. This parameter is mandatory. |
| Incoming Mail, Retrieval interval | Mail retrieval period. By default, the account is checked for presence of new mail every 15 seconds. Some POP3 mail servers may be configured to lock out accounts that access mailboxes at this rate due to excessive activity. If this is the case, use this parameter to increase the retrieval period to any value between 15 and 86400 seconds. |
| Incoming Mail,
Enabled |
Indicates whether the account is currently enabled. Accounts can be disabled manually or automatically as described below. Accounts can only be enabled manually.
After incoming emails have been retrieved for processing, ServicePattern normally deletes those emails from the mailbox. However, if the POP3 server is configured for read-only access, the emails will stay in the mailbox and will be retrieved repeatedly until the system runs out of disk space. To prevent this from happening, the system will automatically disable the email account if an attempt to delete incoming mail returns an error from the POP3 server. If an account is disabled, you should check the Last error message (see below). If the message indicates that the account has been disabled for the above reason, re-configure your POP3 server for full access, and enable the account manually. |
| Incoming Mail,
Last error |
In case the account has been disabled automatically (see above), this read-only parameter displays the error message that caused the system to disable the account. |
| Test | Use this button to verify the correctness of your connection settings. |
| Services tab | |
| Default service | Email service that will be associated with emails arriving via this entry if categorization rules are not set or do not provide any keyword matches. This parameter is mandatory. |
| Default priority | Queueing priority that will be given to emails attributed to the default service (see above). Priority determines position of the email interaction requesting the default service in the queue relative to email interactions associated with other services but competing for the same agents.
The value range is from 1 (the lowest and the default value) to 100. Unlike other media types, priority of email is absolute, i.e., an emails with a higher priority will always be distributed to a qualified resource before emails with lower priority regardless of the time any of those emails spent in the queue. |
| Customer reply priority | Queuing priority of customer emails related to existing email threads.
The system automatically checks whether an incoming email may be part of an existing email thread (e.g., after receiving a reply to an original email request, the customer may have additional questions). Such emails bypass the keyword-based analysis. Instead they are automatically attributed to the same the service as the original request. This parameter allows you to distribute such emails with a higher priority than any new email requests. For more information about email priority, see description of the Default priority setting. |
| Optional Filters | List of filters that will be used to assign emails arriving at the given email scenario entry to different services using keyword-based analysis of the email subjects and body text.
To add a filter, click add. Filters are checked for possible keyword matches in the order in which they appear on the list. As soon as a match is found, the corresponding service and priority will be assigned to the email interaction. Note that this order may be affected by the language setting of the filter. See description of the Language setting for more details. Newly created filters will appear at the end of the list. To change position of a filter in the list, drag it to the desired location. To edit or remove an existing filter, hover over it and select the desired function. |
| Language | Select the language in which the keywords of the given filter will be written. This setting only matters if filter’s keywords may have different meaning in different languages. Otherwise, leave this parameter set to the default value <Any>.
Initially, the system will try to detect the language of the email text automatically. If the language is not identified, only the filters set to Any will be checked for keyword matches. If the language is identified, the system will first check the filters set to Any and then check the filters set to the detected language. |
| Keywords | Specify the keyword expression. Each keyword/phrase in the expression must be set in quotation marks. Logical expressions can include logical operators AND, OR, XOR, NOT, and parentheses. For example: “connection loss” AND (“router” OR “modem”). |
| Service | Select the email service that will be associated with email interactions matching this filter. |
| Priority | Specify the priority that will be assigned to email interactions matching this filter.
For more information about email priority, see description of the Default priority setting. |